Comment choisir des outils d'assistance pour gérer plus de 10 000 périphériques réseau ?
Managing over 10,000 network devices requires a structured, automated, and efficient approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to choose and implement the right tools to streamline this process.
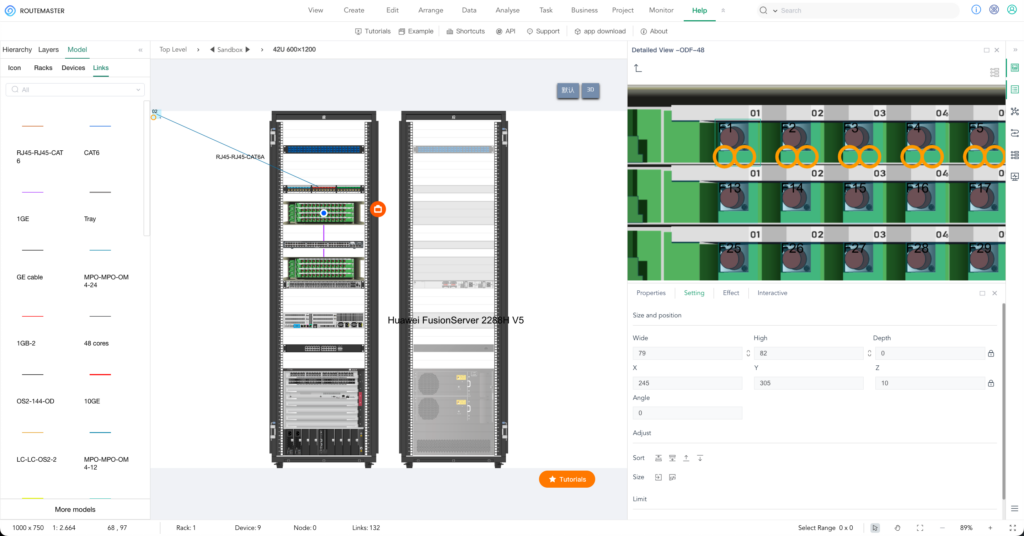
1. Create a Comprehensive Equipment Archive
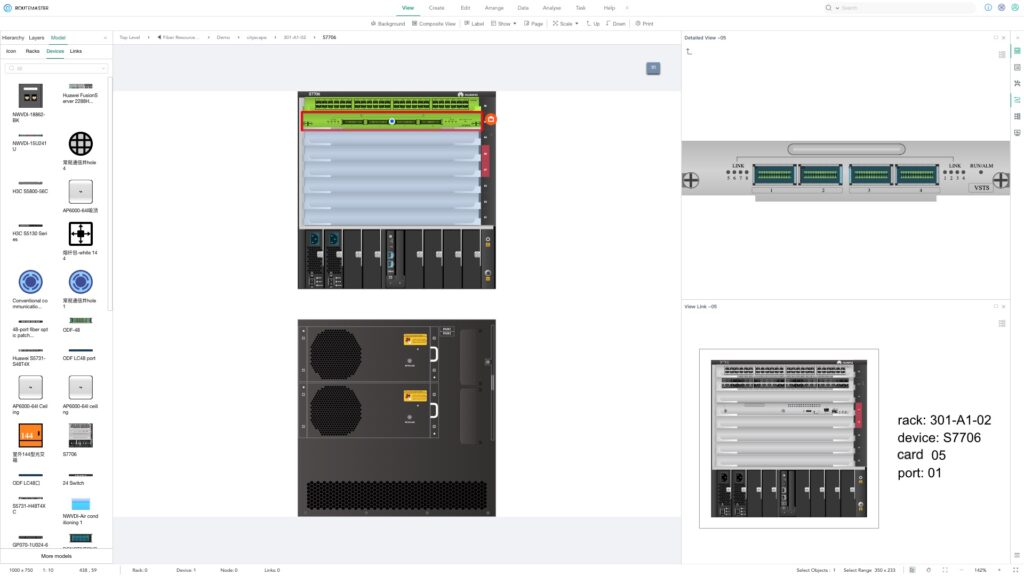
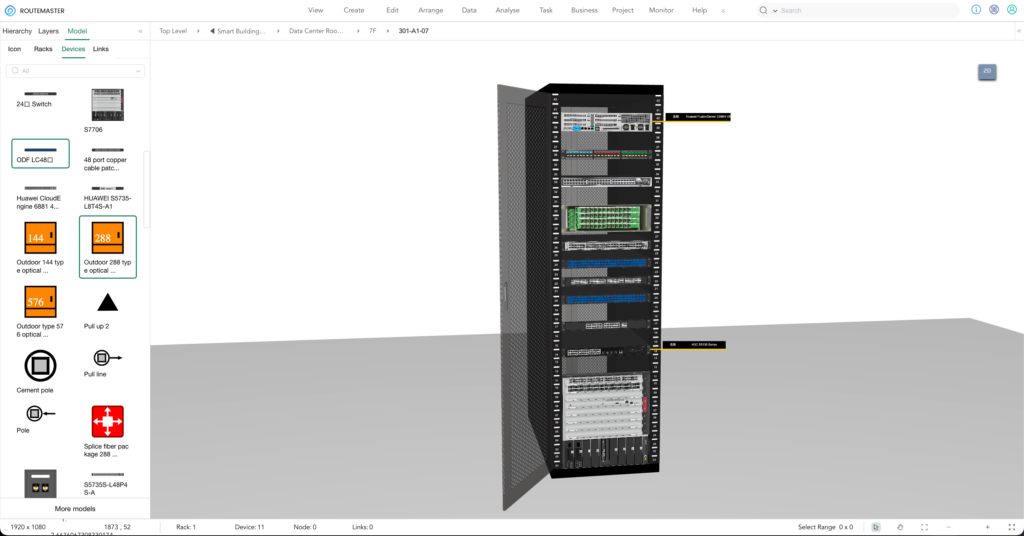
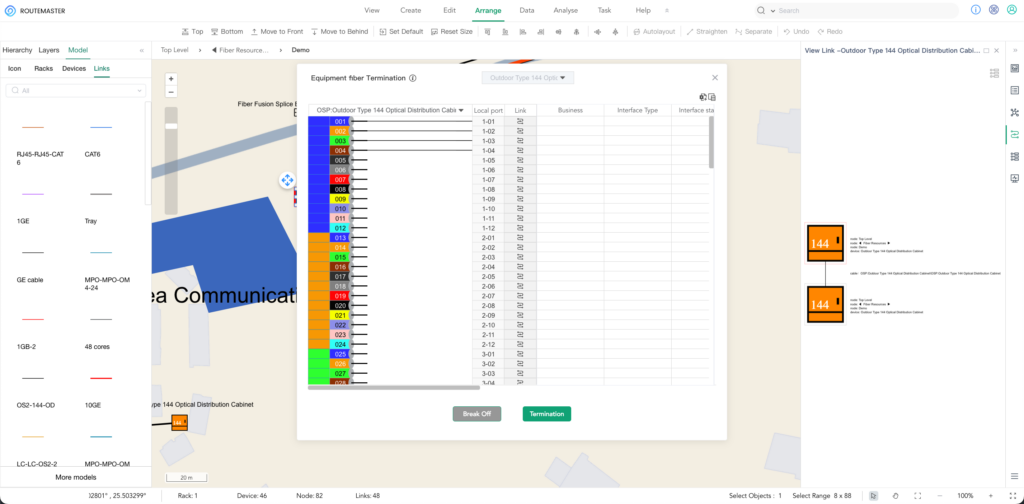
– Device Information:
Maintain a detailed record for each device, including its type, model, serial number, purchase date, department, and location.
– Best Practice Tool:
Use ROUTEMASTER to visually document device information, physical locations, and connection details.
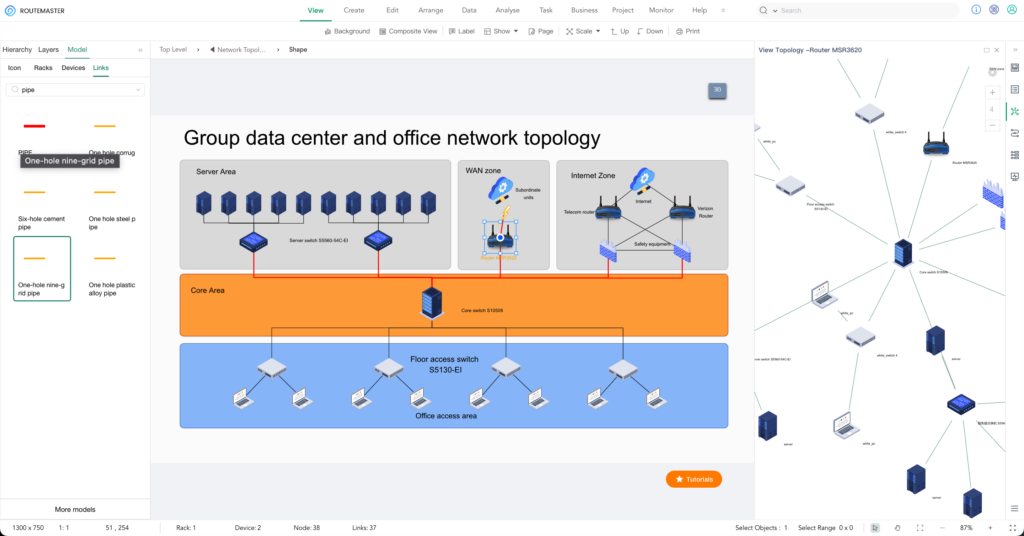
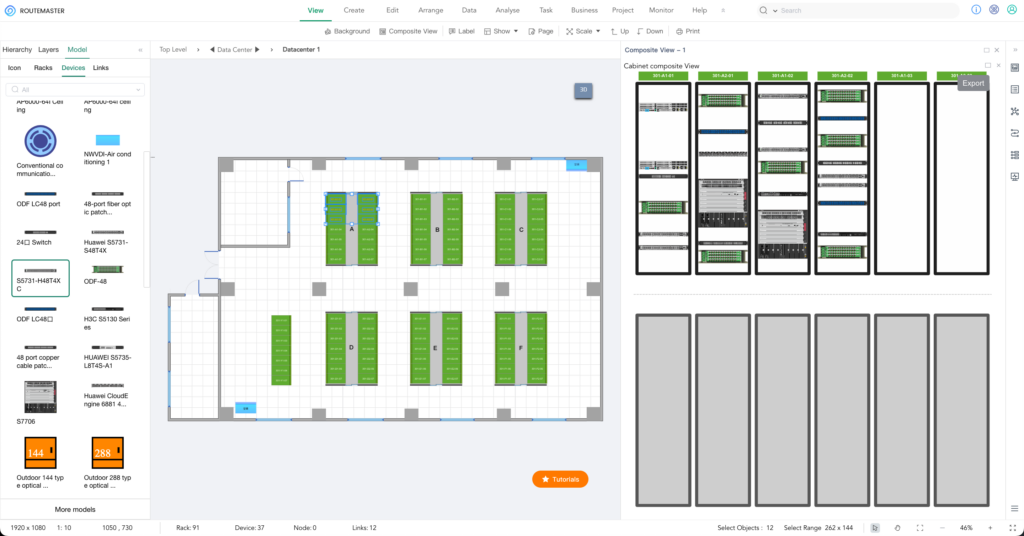
2. Plan Network Topology
– Device Layout:
Strategically plan the placement of devices based on your network’s scale and business needs to ensure a logical and manageable structure.
– Network Topology Diagram:
Draw detailed diagrams that include the backbone network, devices, and cables. These diagrams help your team understand the network layout and quickly locate any issues.
– Best Practice Tool:
ROUTEMASTER can replace Visio, offering advanced features like multi-level topology management and team collaboration. When integrated with monitoring systems, it also enhances alarm location and fault response.
3. Implement Unified Monitoring
– Choose Monitoring Tools:
Select tools that can monitor device status, performance, and security in real-time, based on the scale and type of equipment.
– Unified Monitoring Platform:
Centralize all monitoring data on a single platform to allow real-time data display, alarm notifications, and historical data queries.
– Monitoring Strategies:
Develop tailored strategies, including specific targets, indicators, and alarm thresholds.
– Best Practice Tool:
Consider ZABBIX for open-source monitoring or vendor systems like Cisco, Huawei eSight, H3C IMC, or Ruijie Enjoy Network, Juniper.
4. Automate Operations and Maintenance
– Automated Scripts:
Use scripts to manage multiple devices simultaneously, performing tasks like configuration backups, firmware updates, and patch installations.
– Automated Fault Handling:
Implement automated responses for predictable issues, such as restarting services or switching to backup links, to reduce manual intervention.
– Best Practice Tool:
Ansible is an excellent choice for automating network tasks. It’s easy to use, agentless, and scalable, making it suitable for everything from traditional CLI/SNMP devices to modern API-driven networks.
6. Manage Network Security
– Security Policies:
Establish policies that include access control, intrusion detection, and data encryption tailored to your business needs and network environment.
– Vulnerability Management:
Regularly scan devices to identify and address security vulnerabilities.
– Best Practice Tool:
Use Wireshark and Sniffer to capture and analyze network packets, and Nmap to detect hosts and open ports, helping to identify network issues and security threats.
8. Train and Manage Personnel
– Skill Development:
Regularly train and assess your operational team to enhance their skills and overall capability.
– Clear Responsibilities:
Define clear roles and responsibilities within the team to ensure accountability for each task.
By following these strategies and leveraging the right tools, you can achieve efficient, systematic, and automated management of over 10,000 network devices, ensuring your network remains stable, secure, and efficient.