Cómo supervisar sus recursos de fibra en tiempo real
As a critical part of communication infrastructure, real-time monitoring of optical fiber resources is essential for efficient operation and management. But what are the commonly used monitoring metrics and methods? Let’s explore the key dimensions.

Dimension 1: Resource Quantity
This involves creating a comprehensive archive of your fiber resources, including cable models and routes, the location of optical cross-connect boxes and fiber splicing points, and the connections and terminations of cables.
- Method: Construction documents should be promptly archived in a fiber GIS resource database. Multi-dimensional reports can be generated from this database to track changes in resource quantity over time.

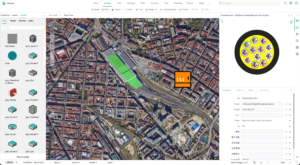
Dimension 2: Resource Capacity
This focuses on analyzing the occupancy, idle capacity, and damage status of fiber cores.
- Method: Map new service links to fiber cores and mark them as occupied. During fault monitoring and inspections, mark damaged fiber cores when detected. Real-time statistical analysis of capacity is performed through reports.
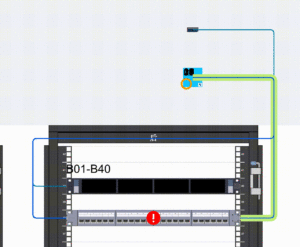
Dimension 3: Resource Failure
Monitoring interruptions and attenuation of fibers ensures their performance meets standards.
- Method: Real-time monitoring via online OTDR is possible, though costly for many operations. A cost-effective alternative is to install transceivers at both ends of the fiber and monitor real-time DDM optical power changes. When attenuation reaches a threshold, an early warning is generated. For sudden interruptions, offline OTDR can be used to locate the fault in the GIS resource database.

 Dimension 4: Resource Maintenance
Dimension 4: Resource Maintenance
Active devices along the fiber link require real-time monitoring. Abnormal indicators like CPU, memory, temperature, and fan issues should trigger alarms. Additionally, critical devices needing routine maintenance should generate reminder events.
- Method: SNMP and other protocols can be used to collect device status data and generate alarms when thresholds are exceeded. A daemon process can be set to determine maintenance cycles and issue reminders.

Dimension 5: Service Monitoring
Changes in business activity, such as the number of customers and revenue, can also be monitored.
- Method: Regularly collect business data to create multi-dimensional trend curves that support informed management decisions.
Here’s a suggestion for an introduction and conclusion tailored to your article, incorporating how ROUTEMASTER can meet the described requirements.
Introduction:
In today’s fast-evolving telecommunications landscape, optical fiber networks form the backbone of connectivity. Efficient management and real-time monitoring of fiber resources are critical to maintaining optimal network performance and preventing costly downtime. However, with increasing network complexity, managing these resources requires more than just manual processes—it demands advanced tools that provide visibility into the network’s condition at all times. This article explores the key dimensions of monitoring optical fiber resources and how leveraging cutting-edge software solutions like ROUTEMASTER can help achieve these goals.
How ROUTEMASTER Can Accomplish These Features:
Resource Quantity and Capacity: ROUTEMASTER archives detailed information about fiber routes, cross-connect locations, and cable terminations in a real-time GIS resource database. It also supports multi-dimensional reporting to track changes in resource quantity and core occupancy.
Failure Detection: Using transceiver-based monitoring, ROUTEMASTER enables real-time fiber performance tracking and attenuation detection, generating early warnings when thresholds are exceeded.
Resource Maintenance: ROUTEMASTER can monitor active devices on the fiber link using SNMP, sending alerts when critical thresholds like CPU or temperature are crossed. It also provides automated reminders for scheduled maintenance events.
Service Monitoring: ROUTEMASTER regularly collects service data, enabling businesses to analyze trends such as customer growth and service utilization, providing valuable insights for better decision-making.
Conclusión:
Effective monitoring and management of fiber resources can drastically reduce operational inefficiencies and prevent network failures. From tracking resource quantity and capacity to monitoring real-time failures and ensuring timely maintenance, the ability to stay on top of your network is crucial. With ROUTEMASTER’s comprehensive network planning, documentation, and monitoring capabilities, organizations can seamlessly manage their fiber infrastructure. Its real-time GIS-based resource tracking, advanced reporting, and fault detection tools enable network operators to optimize their resources and ensure uninterrupted service delivery.